During industrial processes, various harmful gases, vapors, and dust are released into the air. In rooms with a high concentration of people, heat, moisture, and carbon dioxide are also generated, altering the chemical and physical properties of the surrounding air.
If the air composition and cleanliness constantly deviate from permissible limits, it can harm human health, reduce work productivity, and disrupt normal industrial operations.
A ventilation system is designed to remove contaminated air from a space and supply fresh air, ensuring an optimal environment that meets sanitary, hygienic, and technological requirements.
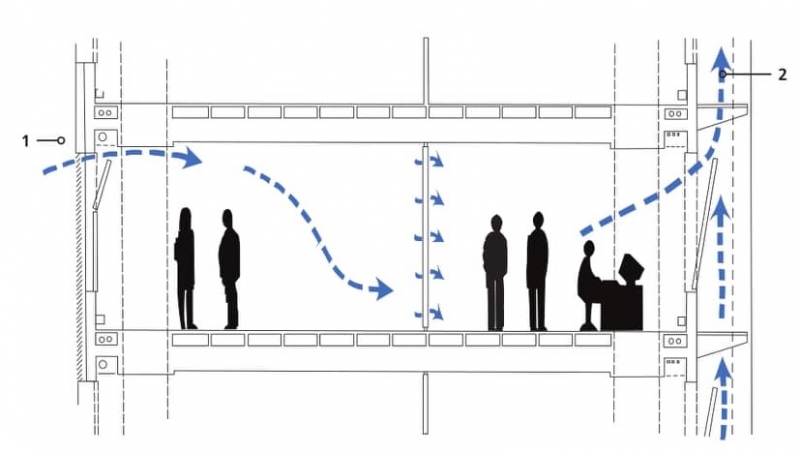
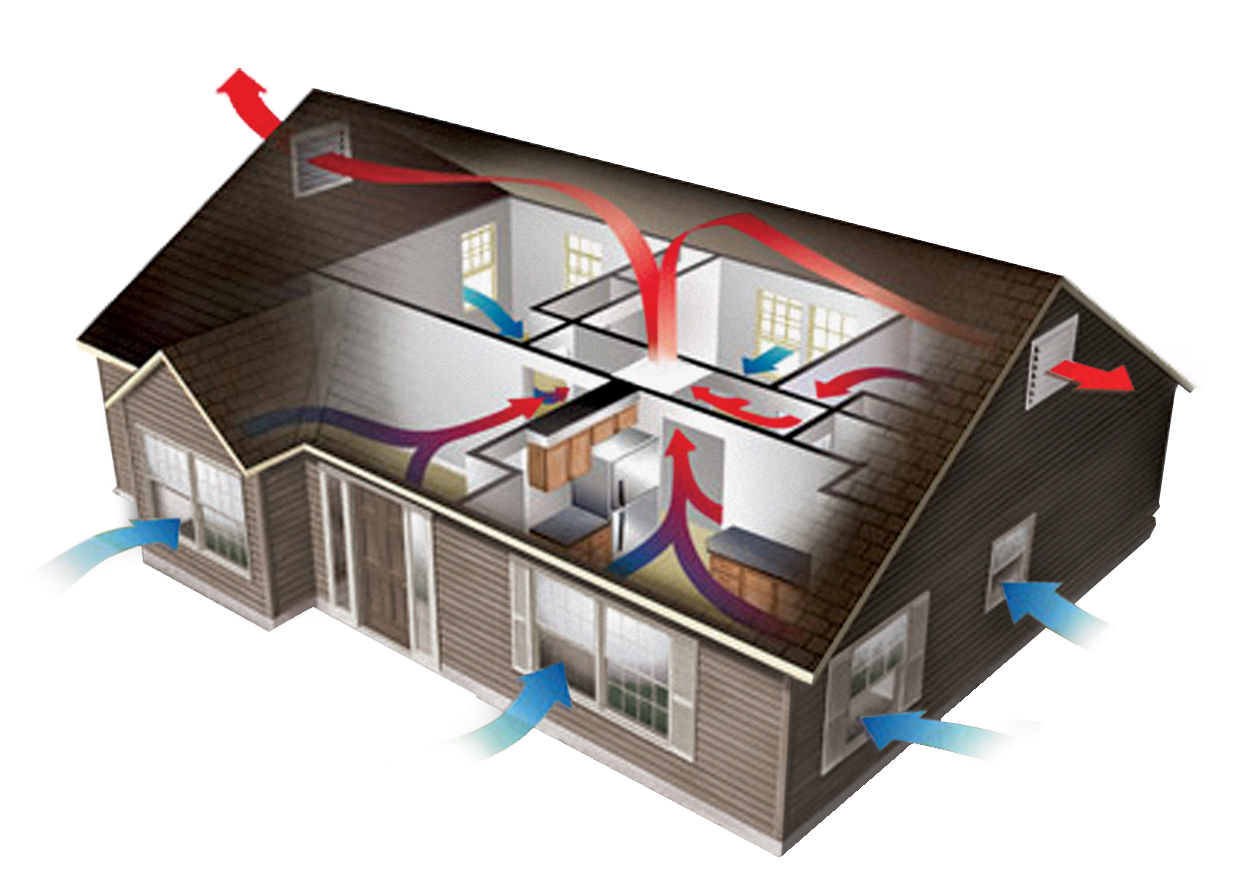
Figure: Air Exchange in a Room
Fresh air supplied from outside
Polluted air removed from the room
A ventilation system is a complex of ducts and equipment designed to ensure the required air exchange in rooms, creating the most suitable air environment for people to live and work in, as well as for industrial processes to function normally. It includes equipment for heating, humidifying, filtering, and purifying the air.
By designing and installing a ventilation system, the air parameters in a room can be consistently maintained at the required level, ensuring a healthy and comfortable environment for work.
Main indicators of indoor microclimate:
Air temperature, °C
Airflow speed, m/s
Relative humidity, %
Dust content
Concentration of harmful gases
Air, as the working medium of the ventilation system, is a mixture of gaseous substances, including nitrogen, argon, oxygen, carbon dioxide, water vapor, helium, neon, krypton, xenon, and ozone.
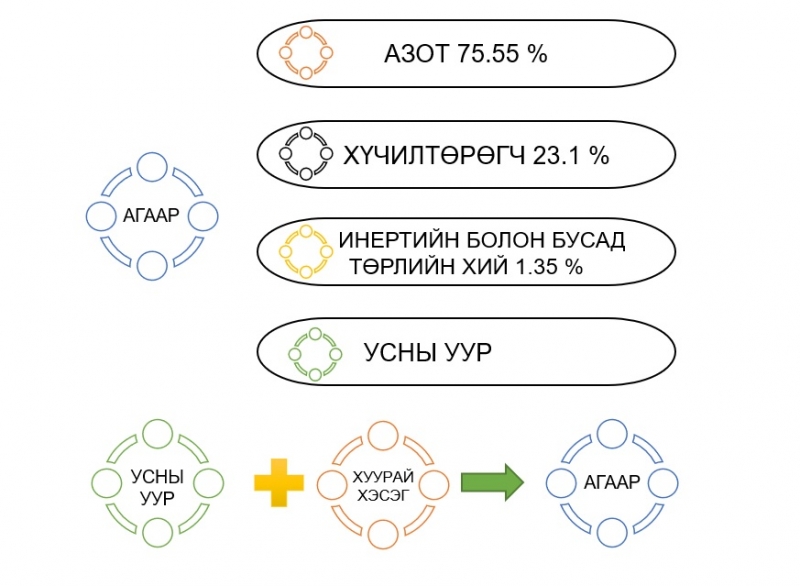
Figure: Air Composition
A ventilation and air conditioning system maintains air parameters within the standard limits to create an indoor microclimate that meets hygiene, health, and industrial process requirements. This ensures that each room in a building has an air environment tailored to its specific function.
Permissible outdoor carbon dioxide content:
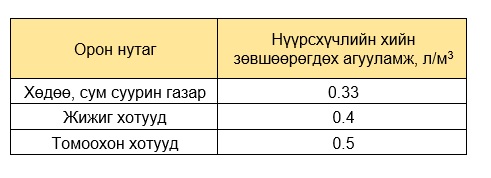
Indoor Air Parameters
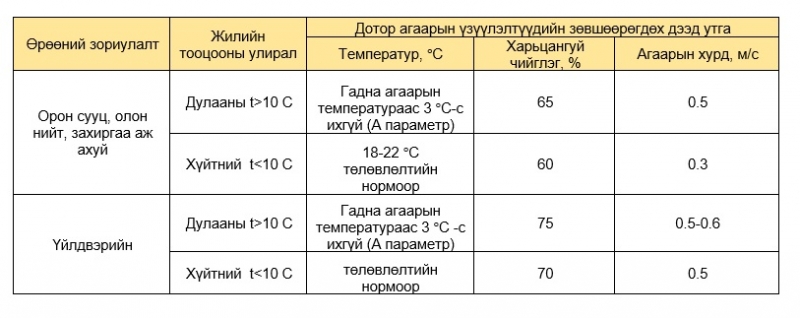
Permissible Indoor Carbon Dioxide Concentration
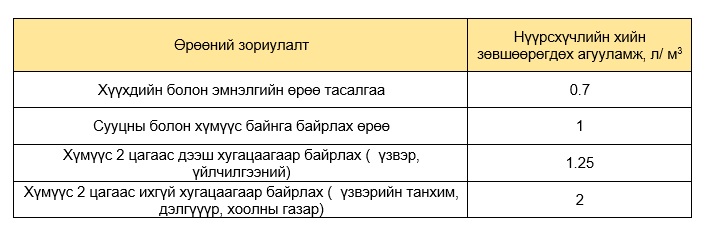
Air Duct Installation and Sheet Metal Thickness Requirements
Air ducts must be installed at the designated level using the connections specified in the design documentation.
The thickness of the sheet steel for air ducts, when the conveyed air temperature does not exceed 800 °C, shall not be greater than the following values:
a. For circular ducts, depending on the diameter:
Up to 200 mm – 0.5 mm
250 – 450 mm – 0.6 mm
500 – 800 mm – 0.7 mm
900 – 1250 mm – 1.0 mm
1400 – 1600 mm – 1.2 mm
1800 – 2000 mm – 1.4 mm
b. For rectangular ducts, depending on the larger dimension:
Up to 250 mm – 0.5 mm
300 – 1000 mm – 0.7 mm
1250 – 2000 mm – 0.9 mm
c. For rectangular ducts where one side exceeds 2000 mm, and for ducts with a cross-section of 2000 × 2000 mm,
the sheet thickness should be determined based on calculations.
For welded ducts, the steel thickness is determined by the welding conditions.
d. For ducts conveying mechanically contaminated (dust-laden) air or air at temperatures above 800 °C,
the steel thickness must be determined based on calculations.
ChatGPT said:
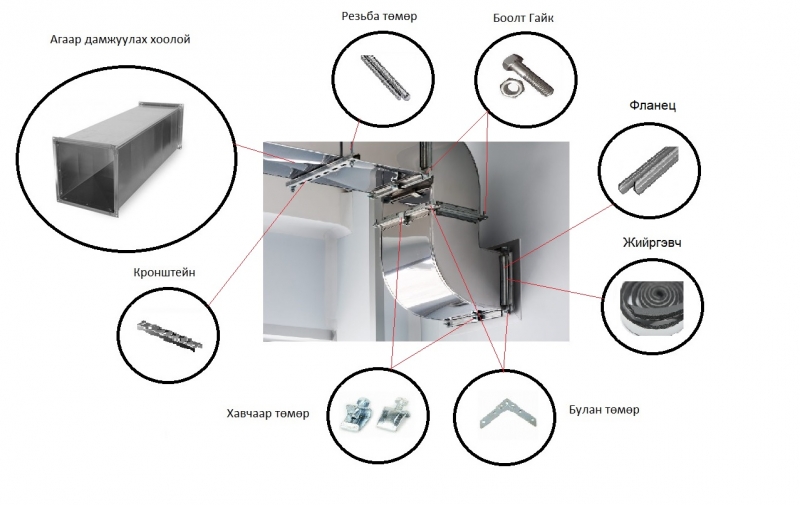
Figure: Ventilation System Installation Materials
In summer, when the outdoor air temperature is high and humidity is high, the air is cooled and dehumidified before being supplied indoors.
In winter, cold air is heated and humidified before being delivered to the room to ensure the required air exchange. Since outdoor air is dry and often contains dust, it must be filtered and cleaned before use.
Types and Classification of Ventilation Systems
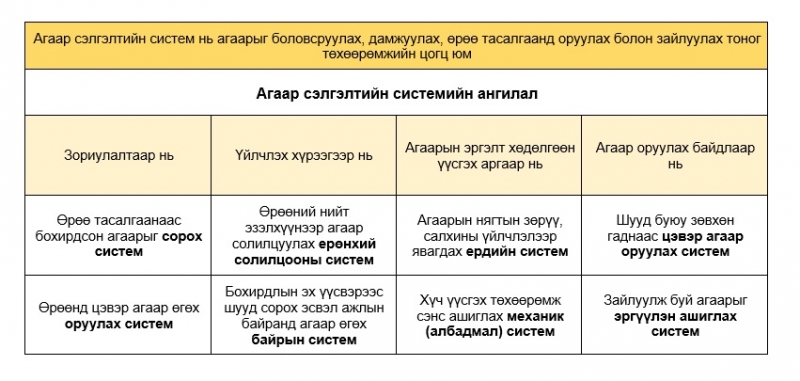
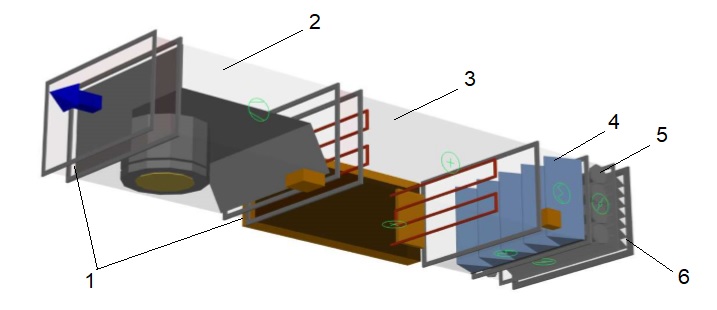
Figure: Structure of the Air Supply System
Flexible connection
Fan
Electric heater
Filter
Automatic valve
Air intake grille
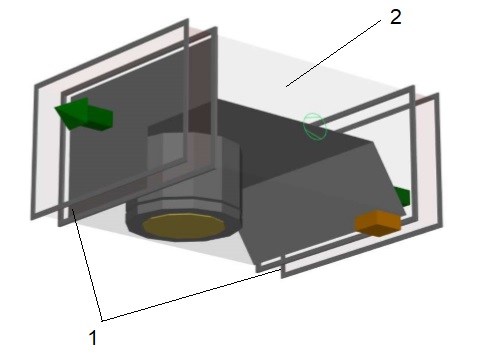
Зураг: Агаар сорох системийн бүтэц
1.Зөөлөн холбоо, 2.Сэнс